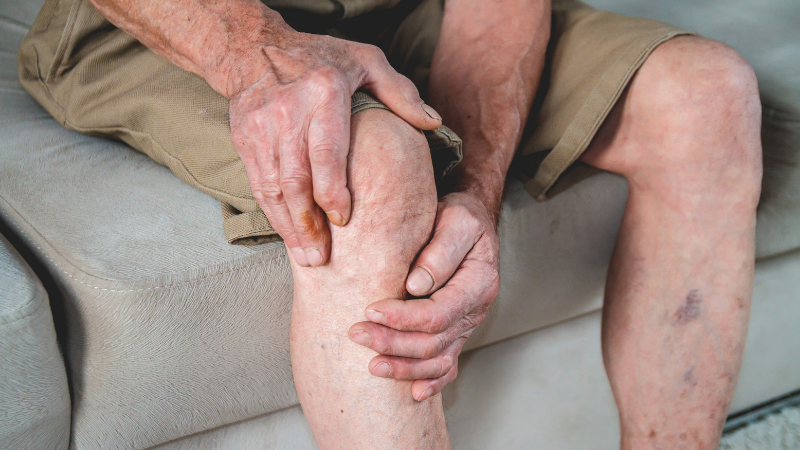
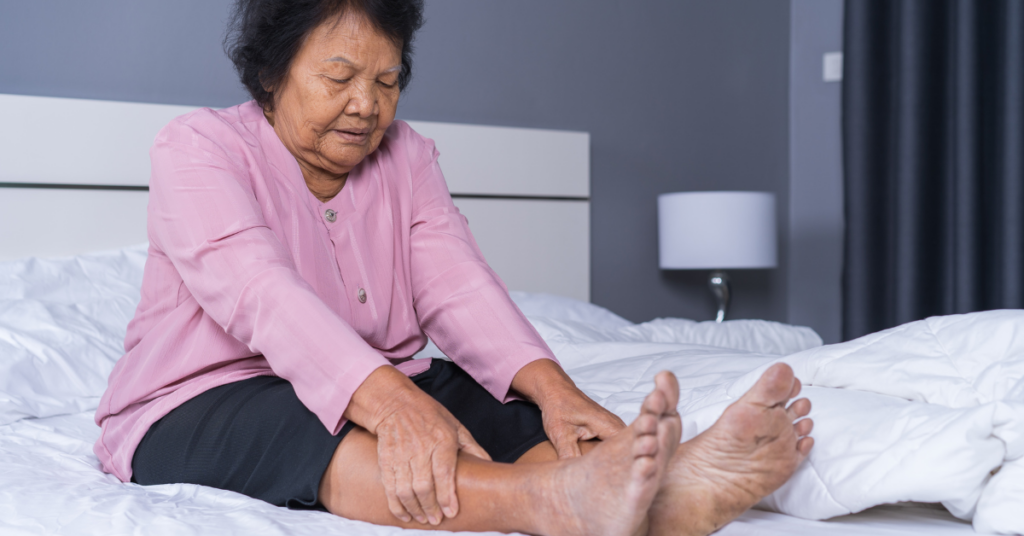
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein in your legs. Deep vein blood clots typically form in your thigh or lower leg, but they can also develop in other areas of your body. DVT affects more than 200,000 Americans each year.
Symptoms
Only 50% of DVT sufferers experience any symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling in your foot, ankle, or leg, usually on one side
- Cramping pain in your affected leg that usually begins in your calf
- Severe, unexplained pain in your foot and ankle
- An area of skin that feels warmer than the skin on the surrounding areas
- Skin over the affected area turning pale or a reddish or bluish color