Fast Facts and Statistics about PAD
- Peripheral Artery Disease affects more than 200 million people worldwide. In the United States alone, PAD affects 8.5 million people aged 40 years and older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- The prevalence of PAD increases with age. It affects 2-4% of individuals aged 50 years or younger, 10-15% of those aged 70 years or older, and up to 25% of those aged 80 years or older.
- Men are slightly more likely than women to develop this condition.
Today, we’re talking about a condition that affects millions of Americans each year – Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). PAD occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to your limbs, and symptoms can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications.
At ECCO Medical, we understand the impact that PAD can have on your life, and that’s why we’re here to provide you with the information you need to manage this condition. In this blog post, we’ll explore the symptoms, causes, and risk factors of PAD and provide valuable insights into the latest treatments available.
Education is key to empowering our patients to take charge of their health, and we aim to be your go-to resource for all things PAD-related. So, whether you’ve just been diagnosed with this condition or are looking for ways to manage your symptoms, you’ve come to the right place.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral Artery Disease, commonly known as PAD, is a circulatory condition where narrowed blood vessels reduce blood flow to the limbs. This happens when fatty deposits build up in the arterial walls.
The primary cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, a systemic condition characterized by plaque buildup in the arteries. This plaque, a combination of fat, cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue, and other substances in the blood, hardens over time, narrowing the arteries and limiting the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the organs and other parts of the body.
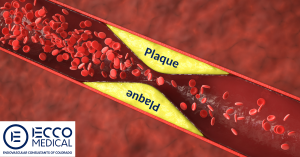
When the arteries supplying blood to the limbs, mainly the legs, are affected, it results in PAD. Over time, this can lead to damage or tissue death due to lack of blood flow and can even escalate to a stage requiring limb amputation in severe cases.
Symptoms of PAD
In some cases, PAD may not show any obvious symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Painful cramping in one or both hip, thigh, or calf muscles after activities such as walking or climbing stairs (claudication)
- Leg numbness or weakness
- Coldness in your lower leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side
- Sores on your toes, feet, or legs that won’t heal
- A change in the color of your legs
- Hair loss or slower hair growth on your feet and legs
- Slower growth of your toenails
- Shiny skin on your legs
- No pulse or a weak pulse in your legs or feet
However, when a person’s arterial blockage progresses to an advanced stage, they may experience a variety of symptoms caused by reduced blood flow to the legs and feet, which can lead to tissue damage and other complications.
One common symptom is intermittent claudication, which is when a person experiences cramping or leg pain while walking or exercising because the leg muscles are not receiving enough oxygen due to reduced blood flow.
In addition to pain, advanced-stage PAD can also cause numbness or weakness in the legs and feet due to nerve damage caused by insufficient blood supply.
In severe cases, PAD can lead to open sores or wounds on the legs and feet that are slow to heal. These wounds can become infected, causing further complications. In some cases, a person may also experience changes in the color or temperature of the skin on their legs and feet due to reduced blood flow, which can result in pale or bluish skin and cold extremities.
These symptoms can greatly impact a person’s quality of life as they may have difficulty walking or performing daily activities without experiencing pain or discomfort.
Clinic Overview of Advanced PAD
The progression of advanced-stage PAD occurs gradually over time. As plaque continues to build up in the arteries, it restricts blood flow even further. This causes weakened muscles and tissues in the legs and feet and nerve damage.
If left untreated, advanced-stage PAD can lead to serious complications such as critical limb ischemia (CLI). CLI is characterized by severely restricted blood flow, which can result in tissue death and ultimately require surgical intervention or even amputation.
Furthermore, advanced-stage PAD increases a person’s risk for heart attack and stroke. The same blockages that occur in the leg arteries can also happen in the arteries leading to the heart and brain, increasing the likelihood of these life-threatening events.
Risk Factors for Advanced PAD
There are several risk factors for advanced PAD, including obesity, family history, smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes. Other factors, such as age and lack of physical activity, can also contribute.
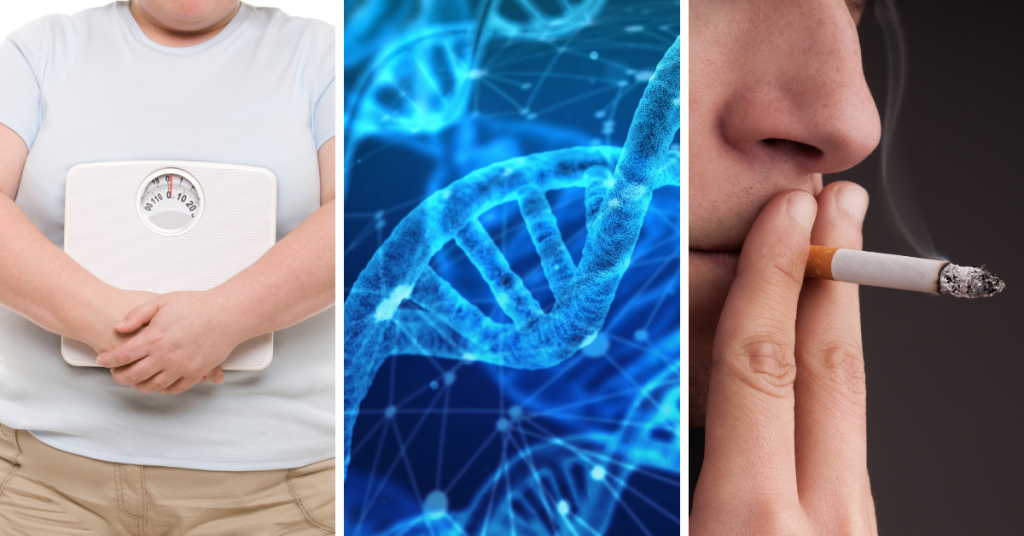

- Obesity is a significant risk factor for advanced PAD as it increases the strain on the arteries and can lead to a buildup of plaque.
- Family history also plays a role in the development of PAD, with studies showing that individuals with a family history of the condition are at higher risk. This suggests that genetics may play a role in predisposing individuals to PAD.
- Smoking is another crucial risk factor for advanced PAD. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the arteries, leading to inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels. This can impede blood flow and increase the risk of developing advanced PAD.
It is essential to note that diet and lifestyle choices can also contribute to the development of advanced PAD. A diet high in saturated fats and cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries. At the same time, a sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of obesity and other health conditions that are associated with advanced PAD.
Advanced PAD does not occur quickly; it develops over time due to a gradual plaque buildup in the arteries. This process may take years or even decades before symptoms become noticeable. However, early detection and treatment can help prevent further complications.
Patients with a family history of PAD should be proactive about their health by making healthy lifestyle choices such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing other underlying health conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. It is also advisable for these individuals to undergo routine screenings for early detection and monitoring for any signs or symptoms.
ECCO Medical Can Help

Patients needing treatment for leg pain, calf pain, or leg cramps at night need look no further. ECCO Medical is the leading Colorado PAD treatment center, providing numerous minimally invasive therapies, including:
Balloon Angioplasty – Balloon angioplasty involves inflating a small balloon in the affected artery to widen it and improve blood flow.
Atherectomy – This procedure aims to remove plaque buildup in the arteries and is most commonly done in the legs, but can also be done in the heart. It is performed with specialized catheters that have laser or grinding functionality.
Stent Placement – If angioplasty or atherectomy aren’t successful in restoring flow through an artery, a stent, or a tube made of metal wire, is placed to keep the vessel open. This is a permanent implant.
These are usually performed as outpatient procedures in our clinic with sedation. The procedures usually take between one and four hours, depending on the complexity.
To find out if you’re a candidate for one of these interventions, take the quiz!